Table of Contents
The Complete Beginner’s Guide to Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi or Decentralized Finance is a global financial system that lifts the grip of banks and institutions over financial services using technology similar to cryptocurrencies, distributed ledger technology, blockchain, smart contracts, and such.
Much of the technology in the DeFi space aims to improve the current financial system, potentially improving the user experience (for both businesses and their clients). Thanks to DeFi’s dependence on blockchain technology, transactions are completed faster, cheaper, and — in some cases — more securely than they would with human intervention.
Since they require much less maintenance work, decentralized exchanges typically have lower trading fees than centralized exchanges. On the other hand, centralized finance exchanges function as a middleman and control your crypto transactions and activity.
That results in the elimination of fees that heavily burden banking and financial services. DeFi handles money you control instead of handing it over to a bank. You just need an internet connection, so the level of privacy is higher than in a bank.
The core benefit of DeFi is easy access to financial services, especially for those who are isolated from the current financial system.
Traditional finance relies on institutions such as banks to act as a central authority, and courts to provide arbitration. DeFi applications are financial applications that do not need any intermediaries or arbitrators.
In short, decentralization means that no chief body controls something. To an extent, banks and other financial institutions have power over your funds. These entities can freeze your assets, and you are at the mercy of their hours of operation and cash reserves.
One of the many advantages of DeFi over the traditional financial system is that if you need a loan, there is no official body to scrutinize your life and rank your credit score. You just need to provide collateral.
The decentralized exchange allows you to trade digital assets on a decentralized market without a trusted intermediary to hold your funds. All the transfers are done in seconds, minutes at worst. The trades are made directly between user wallets with the help of smart contracts.
DeFi’s smart contracts are designed to take the place of traditional financial systems. While a usual contract uses legal terminology to specify the terms of the relationship between the entities entering the contract, a smart contract uses computer code. The downside of that is that, like any computer code, smart contracts can be vulnerable to both unintended programming mistakes and malicious hacks.
And you can invest, save, and harvest yields like nothing traditional banks can offer. And while some see DeFi space as the future of finance, others consider it a threat to the global financial system.
In this beginner’s guide to decentralized finance (DeFi), we’ll first learn what DeFi protocols are and after that, we will show you how to invest in decentralized finance (DeFi).
How To Use DeFi Protocols
Understanding DeFi and blockchain technology can be tricky. Not every coin operates on its network, and things get even more complicated when we start reading about layers and such.
Well, the easiest is to imagine a blockchain network as a mini-Internet. For example, the Ethereum blockchain is a web of computers (nodes). It’s widely used across the DeFi ecosystem.
The most significant power of this network is the ability to execute smart contracts, for example, special computer programs which automatically perform when conditions are met.
These smart contracts enable DeFi developers to build more sophisticated functionality than simply sending and receiving digital currency.
DeFi protocols have simply put a set of rules and regulations executed by autonomous programs and algorithms that enable particular tasks and activities. These protocols are in charge of handling different financial activities, swapping crypto tokens, automated lending, and decentralized borrowing, providing ways to move tokens from network to network, etc.
To enable DeFi, smart contracts automatically execute financial transactions among participants. When the contract’s conditions are fulfilled, they self-execute their set of instructions. This financial system allows the smart contracts on the blockchain to take the place of trusted intermediaries.
Many protocols started on Ethereum, growing in time to be their own separate networks like Avalanche did.
If this gave you a headache, don’t worry. We will use the term DeFi protocol to denote different platforms you can use to earn money, crypto exchanges, yield farming, lending protocols, etc.
What are some of the leading DeFi Protocols? Decentralized lending protocols and yield farming Aave, Compound, and Maker are the major DeFi lending protocols, with billions of dollars worth locked up in their smart contracts.
How Does DeFi Work?
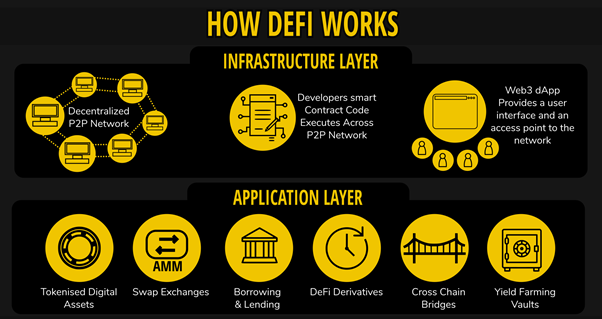
It’s not easy to digest, but it is easy to navigate if you follow this beginner’s guide.
What are DeFi tokens?

Various DeFi protocols use their own tokens. Some of them are used for governance. Namely, holders of these tokens can participate in running the protocol. Think of those as voting power when it comes to vital questions about the future of the network or protocol in question.
DeFi tokens are better known as – altcoins – because they are alternative coins to Bitcoin and Ether. For example, Aave is a decentralized lending protocol that allows DeFi users to deposit their crypto to earn interest, and manipulate an automated system of smart contracts. Their token is AAVE, and you can hold it, stake it, trade it, swap it, buy or sell it, just like any other crypto coin.
Why does this matter? Because the first step to getting started in DeFi is deciding which decentralized exchange you want to begin with and – obtaining the native token of that platform.
That, in turn, determines which wallet you will need to open if you haven’t already. Wallets are locations for holding and transacting digital assets. Make sure the wallet is compatible with DeFi applications (decentralized applications).
Here’s one example. AAVE tokens are kept in the Aave wallet. It’s much self-explanatory how to invest in decentralized finance if you don’t have tokens to invest!
Other popular DeFi applications are DEXs and lending pools.
Let’s get started.
First steps: Lending platforms
The quickest, safest way to start investing with decentralized finance (DeFi) is crypto lending. How does a bank make money? They take your deposit, give it to big financial players, then take the lion’s share and give you that few fractions of a percent as your interest on your savings.
By cutting out the middleman, decentralized finance (DeFi) lending platforms let you deposit your cryptocurrency, automate connecting you with borrowers, then share the profit with you, resulting in interest rates that seem sky-high compared to the traditional financial system.
But why is decentralized lending even useful? The answer is that it’s a massively scalable application. A crypto service that makes more interest than traditional bank accounts with lower risk could in theory attract billions in deposits.
Do your research first.
Things move very fast in the crypto world, doubly so when it comes to decentralized finance. By the time you read this, specific data, like prices and rates, could change, so always do your homework and research first.
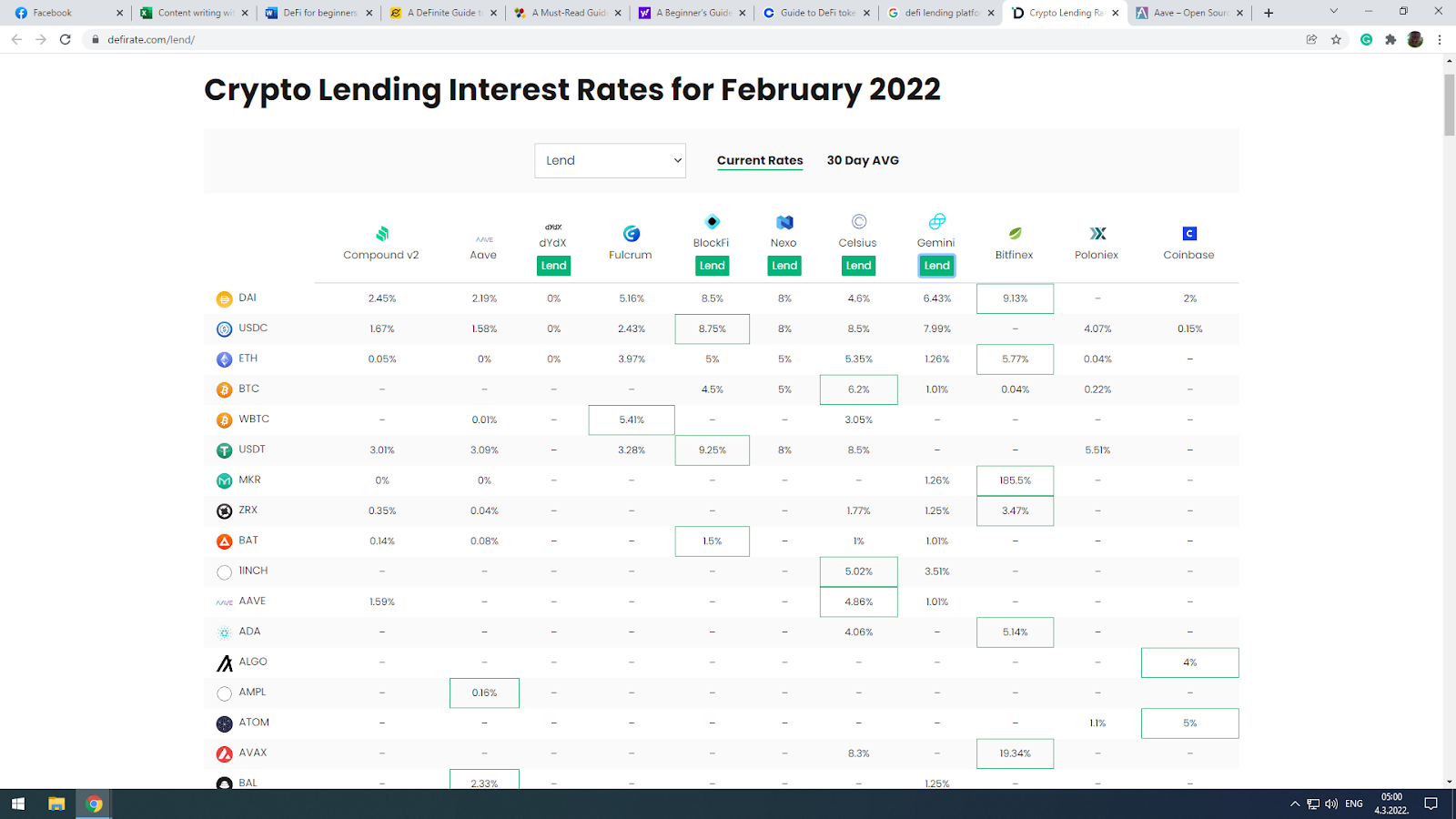
Lending rates differ from platform to platform and from coin to coin.
Check the current interest rates on different platforms. Not every crypto coin has the same lending interest rate. Buy the relevant coin for the DeFi protocol you plan to use. If you already have a wallet and crypto funds, it is easiest to start with that coin.
Let’s say you have Tether (USDT). It’s a decentralized stablecoin. That means the value is always 1$. Many beginners start with stablecoins to offset the volatility of cryptocurrencies. Nothing is more disheartening than seeing your favorite coin plummet in value, just as you’ve deposited it, hoping for that sweet passive income trickling in.
Next, you want to check with individual lending platforms for current rates. For example, the list above states that BlockFi offers 9.25% APR, while, actually, they offer only 8%, and Celsius offers 8.5%. So, double-check all the data.
When you find the best deal, register with that lending platform. That is usually done by only registering with your email and running through a simple verification protocol for your safety. The next step is connecting your e-wallet with the selected platform. Decide on the sum you want it to deposit you, and there you go!
How to invest in DeFi fastest and safest? Lending is the way to go.
Here is a checklist for your convenience:
- Visit lending platforms to check their rates for cryptocurrency
- Try one of the following:
- Compound
- Aave
- BlockFi
- Nexo
- Celsius
- Biftinex
- Coinbase
- Find the token with the highest interest rate (expressed as either APY or APR)
- Try one of the following:
- Do you have that cryptocurrency?
- No?
- Create a wallet at crypto exchange (Binance, Coinbase, KuCoin, Kraken)
- Buy cryptocurrency via bank transfer, credit card, or P2P transfer.
- Yes?
- Register at the lending platform of your choice
- Connect the wallet with your crypto funds
- Deposit desired sum
- Earn interest
- No?
Going deeper: Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools provide liquidity for decentralized exchanges (DEXes) so that customers can swap cryptocurrency tokens. Remember, this is banking without the bank. So, if a user wants to trade Ether (ETH) for Tether (USDT), the system needs to have actual tokens – liquidity – to perform the exchange.
To become part of a pool, liquidity providers can send specific funds to a smart contract and receive pool tokens in return, earning passive profit based on the fees traders pay when they interact with that pool. Pool tokens are the key component to getting your deposited funds back.
Yield farming is another activity in the DeFi space that involves searching for profit via various DeFi projects.
The same underlying technology is a bit abstract because buyers and sellers are not connected. For example, if a user buys a token, there isn’t a seller on the other side in a traditional world. The activity is, instead, managed by an algorithm that governs what’s going on in the pool. Of course, the tokens sold or bought need to come from somewhere, and that’s where you as one of the liquidity providers, intermediate.
Basically, you invest an equal amount of tokens to be swapped. In the above case, you would deposit an equal value of ETH and USDT and contribute it to the ETH-USDT pool. Usually, you are then given a Liquidity Provider (LP) token as proof that you participate in the pool with your share, which can earn you a percentage of trading fees when customers swap ETH for USDT (in this case) but also other rewards like governance tokens.
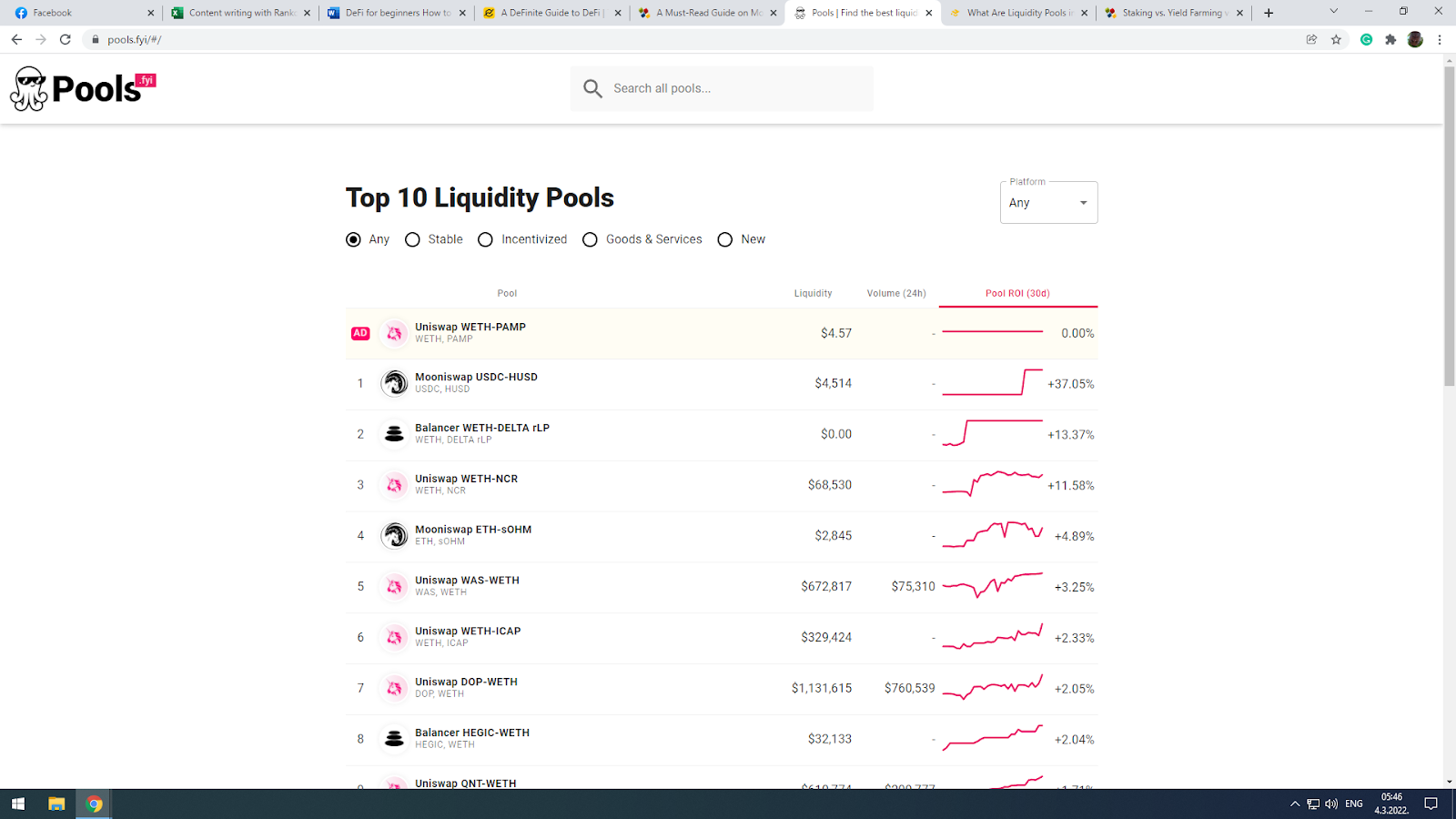
Notice that pools are always a pair of crypto coins.
Risks are more significant than those with crypto lending, but the rewards are also higher. First, there is a risk of tokens in a pair losing value. Then there is a risk of pairing with a token that loses all its value. Beware of rewards paid in the project’s native token. Then you provide assets and collect coins that are either worthless or could become worthless. If a pool has become particularly hot, many new providers can join, lowering the yield.
If you provide liquidity for decentralized stablecoins like USDC, Tether, or DAI, you can avoid having a single point of failure, but the rewards are significantly lower, too.
The process is slightly more complex because you need to have TWO coins in a 50/50 value position. So, if you want to provide liquidity for ETH-USDT, you must have both assets in your wallet, decide on the platform, and deposit both crypto coins to get an LP token. Different swap exchanges handle the actual steps slightly differently, so make sure you do your homework and check how your DeFi platforms of choice regulate it.
Here is a checklist for your convenience:

Find the pool you want to participate in at one of the following exchanges:
- Curve
- Uniswap
- Sushiswap
- Balancer
The ultimate stage: Yield Farming (Liquidity Mining)

Yield farming is a practice of locking in crypto assets for maximum yield. Where lending was the most similar to a savings account, liquidity pools have no actual counterpart within the traditional financial system. But in both cases, you retain full mobility of your funds. With yield farming, it’s more like lending the money to the bank while utilizing every possible trick and strategy to gain the most from your crypto.
Of course, with the high returns comes the increased risk. Above all, the process and procedures of yield farming become complex, giving rise to yield aggregators, platforms that leverage different decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, and strategies to maximize your profits. Aggregators will fine-tune your yields for you, compound rewards, etc.
Investors risk impermanent loss, liquidation, smart-contract, and composability risks. In other words, this is the highest risk, highest rewards stage.
The process itself is similar to a liquidity pool. You will need to find a yield aggregator of your choice. Check the networks you are interested in (Ethereum, Avalanche, Polygon) and see what pairs provide the best APY or daily APR. Yield aggregators offer to buy/swap tokens for your selected pair. If you don’t have enough of coin A or coin B, gain and reinvest for maximum yield.
You can start by researching other aggregators like Harvest Finance, Autofarm, Yearn, and Finance. Proceed with caution.
How to withdraw from DeFi wallet to bank account

Hopefully, you’ve earned a nice passive income. It’s time to reap the rewards and turn your tokens into fiat money. The procedure can be confusing because the tokens you’ve chosen to invest in, may be deposited in some DeFi wallet or obscure coins. To get it to USD, EUR or GBP could take a bit of effort and fees. So, how to withdraw from the DeFi wallet to your bank account?
The first step is to check if your crypto exchange of choice supports the token you want to cash in. Binance, Coinbase, KuCoin, Kraken, or other major exchanges, are suggested for beginners.
If the token is not supported, you want to go to Uniswap (on the Ethereum network) or PancakeSwap (on the Binance network) and exchange your exotic token for stablecoin, like USDT (Tether). On the other hand, there will be a gas fee, so save some tokens native to the platform to pay the fees. That could be outrageously high for networks like Ethereum.
For example, it would take up to $20 or more to perform a token swap on Uniswap (a decentralized exchange), as the Ethereum network has high operating fees.
Once you have cryptocurrency handled by your crypto exchange of choice, make sure you send it to the wallet with the exchange. That will accrue more gas fees, as ‘swap’ and ‘send’ are two different actions.
Some exchanges will ask you to trade your crypto coin for fiat currency using the ‘spot’ trade option. Yet, leading exchanges like Coinbase have the ‘Sell’ tab allowing users to exchange the cryptocurrency to their cash wallet with relative ease. Selecting the ‘Withdraw funds’ will initiate the transfer from the exchange to your bank. More fees could be waiting for you here. It usually takes a few days to collect your cash.
Some platforms offer crypto credit cards. There are crypto ATMs that can speed up the process as well. Hopefully, there is one of these in your city.
Safety considerations

The moment you decide to invest in decentralized finance (DeFi), you have stepped off the beaten track and headed toward the crypto wilderness. As long as you stick with Bitcoin and Ether, holding them in your wallet, you are safe. You might want to try lending these first, though the yields are not as fantastic as with lesser-known altcoins. However, the chances of being scammed or losing money to hidden costs and fees are significantly lower.
If you want to try your hand at DeFi in a safe manner, go with decentralized stablecoins like USDC, USDT, and Dai. They have their value pegged to USD, which means there is no price volatility as they always should be worth precisely 1$.
Then there is a question of networks. Sticking to Ethereum and its decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms includes high fees while, the road is safe, as dealing with more exotic networks brings the necessity to open platform-specific wallets and handle highly volatile tokens. Even if the fees are lower, you could needlessly lose money.
Keep in mind that eventually, you must trade all the yields, rewards, and gains for cash with all the costs of the token swap, selling, and bank transfers. Last but not least, beware of the tax authorities. In most countries, selling crypto is viewed as capital gain and taxed accordingly.
Do you like our guide on decentralized finance and the future of finance? Check out our recent explanation: What Are Crypto Launchpads And How Do They Work.
Crypto Ping Pong Digest
Trash style news. You will definitely like